- 전체
- Sample DB
- database modeling
- [표준 SQL] Standard SQL
- G-SQL
- 10-Min
- ORACLE
- MS SQLserver
- MySQL
- SQLite
- postgreSQL
- 데이터아키텍처전문가 - 국가공인자격
- 데이터 분석 전문가 [ADP]
- [국가공인] SQL 개발자/전문가
- NoSQL
- hadoop
- hadoop eco system
- big data (빅데이터)
- stat(통계) R 언어
- XML DB & XQuery
- spark
- DataBase Tool
- 데이터분석 & 데이터사이언스
- Engineer Quality Management
- [기계학습] machine learning
- 데이터 수집 및 전처리
- 국가기술자격 빅데이터분석기사
- 암호화폐 (비트코인, cryptocurrency, bitcoin)
ORACLE [Oracle] rollup 쿼리 , 오라클 부분합 구하기
2021.09.01 17:36
[Oracle] rollup 쿼리 , 오라클 부분합 구하기
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle ROLLUP extension to generate reports that contain subtotals and totals.
Getting started with Oracle ROLLUP
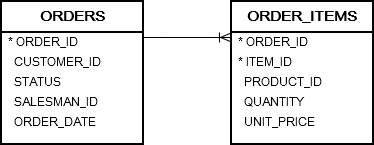
Consider the following orders and order_items tables in the sample database:
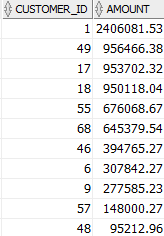
The following query returns the sales revenue by customers in the year of 2017. It calculates net values for the sales orders with the Shipped status and is in charge of a salesman.
SELECT customer_id, SUM(quantity * unit_price) amount FROM orders INNER JOIN order_items USING (order_id) WHERE status = 'Shipped' AND salesman_id IS NOT NULL AND EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) = 2017 GROUP BY customer_id ORDER BY amount DESC; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
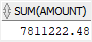
To get the sum of the values in the amount column, you may come up with the following subquery:
SELECT SUM(amount) FROM ( SELECT customer_id, SUM(quantity * unit_price) amount FROM orders INNER JOIN order_items USING (order_id) WHERE status = 'Shipped' AND salesman_id IS NOT NULL AND EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) = 2017 GROUP BY customer_id ); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
Oracle provides a better and faster way to calculate the grand total by using the ROLLUP as shown in the following query:
SELECT customer_id, SUM(quantity * unit_price) amount FROM orders INNER JOIN order_items USING (order_id) WHERE status = 'Shipped' AND salesman_id IS NOT NULL AND EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) = 2017 GROUP BY ROLLUP(customer_id); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
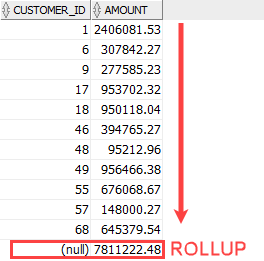
In this query, we used the ROLLUP expression to calculate the grand total of sales amounts of the selected orders.
As shown clearly from the output, the row with a NULL value in the customer_id column denotes the grand total row. The amount column of the grand total row showed the sum of all amounts in the output.
Oracle ROLLUP syntax
The ROLLUP is an extension of the GROUP BY clause. The ROLLUP calculates multiple levels of subtotals across a group of columns (or dimensions) along with the grand total.
The following illustrates the syntax of the ROLLUP :
SELECT col1, col2, aggregate(col3) FROM table_name GROUP BY ROLLUP (col1, col2); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In the query syntax above, the ROLLUP creates subtotals that roll up from the most detailed level to a grand total, following a grouping column specified in the ROLLUP.
The ROLLUP works as follows:
- First, calculate the standard aggregate values in the
GROUP BYclause. - Then, progressively create higher-level subtotals of the grouping columns, which are
col2andcol1columns, from right to left. - Finally, calculate the grand total.
The ROLLUP clause generates the number of grouping sets which is the same as the number grouping columns specified in the ROLLUP plus a grand total. In other words, if you have n columns listed in the ROLLUP, you will get n+ 1 level of subtotals with ROLLUP.
In the syntax above, the ROLLUP clause generates the following grouping sets:
- (col1, col2)
- (col2)
- (grand total)
The number of rows in the output is derived from the number of unique combinations of values in the grouping columns.
To reduce the number of subtotals, you can perform a partial roll up as shown in the following syntax:
SELECT col1, col2, aggregate(col3) FROM table_name GROUP BY col1, ROLLUP (col2); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
More Oracle ROLLUP examples
The following example use ROLLUP to return the sales values by salesman and customer:
SELECT salesman_id, customer_id, SUM(quantity * unit_price) amount FROM orders INNER JOIN order_items USING (order_id) WHERE status = 'Shipped' AND salesman_id IS NOT NULL AND EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) = 2017 GROUP BY ROLLUP(salesman_id,customer_id); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
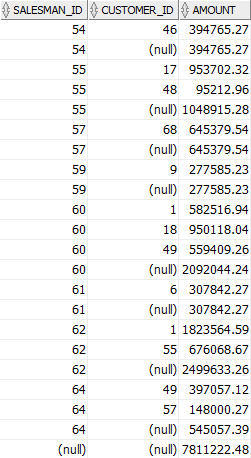
As you can see from the output, the query returned the following set of rows:
- The regular aggregation rows that would be returned by the
GROUP BYclause without using theROLLUPexpression. - The first-level of subtotals aggregating across salesman for each combination of salesman and customer.
- The second-level subtotals aggregating across salesman and customer for each salesman.
- A grand total row.
The following query performs a partial rollup:
SELECT salesman_id, customer_id, SUM(quantity * unit_price) amount FROM orders INNER JOIN order_items USING (order_id) WHERE status = 'Shipped' AND salesman_id IS NOT NULL AND EXTRACT(YEAR FROM order_date) = 2017 GROUP BY salesman_id, ROLLUP(customer_id); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
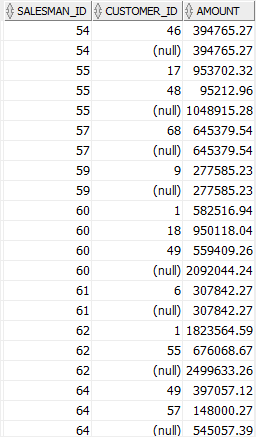
The query outputs regular aggregation rows that would be returned by the GROUP BY clause without using the ROLLUP and the subtotals aggregating across salesman for each combination of salesman and customer.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle ROLLUP to generate reports that contain subtotals and totals.
[출처] https://www.oracletutorial.com/oracle-basics/oracle-rollup/
광고 클릭에서 발생하는 수익금은 모두 웹사이트 서버의 유지 및 관리, 그리고 기술 콘텐츠 향상을 위해 쓰여집니다.


